Ocular rosacea treatment is vital if you develop the condition. Left untreated, it can endanger your eyesight.
This article gives an overview of ocular rosacea. It explains the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of this form of rosacea.
What is ocular rosacea?
Rosacea is an inflammatory skin condition. It commonly affects the forehead, nose, and cheeks, causing redness and pimples. About 60% of people with rosacea have a case that affects the eyes. This is ocular rosacea.
Ocular rosacea is a complex condition. It
It is possible to have ocular rosacea before any skin problems occur.
What are the symptoms of ocular rosacea?
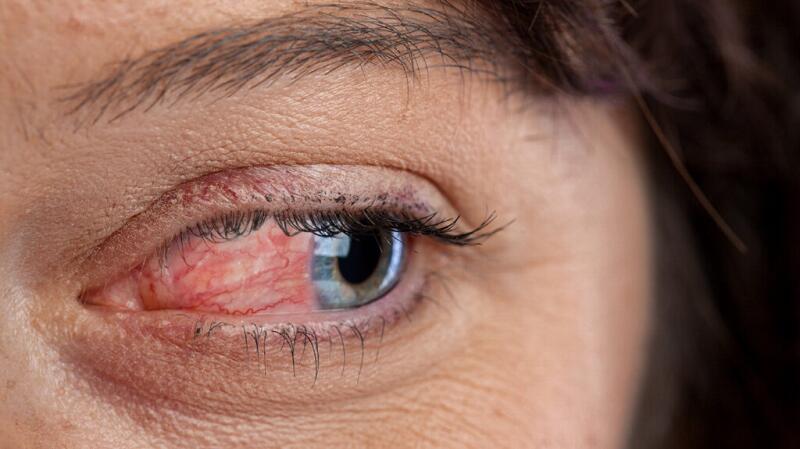
Ocular rosacea can affect the eyes, eyelids, and areas around the eyes. Various symptoms can develop, including:
- bloodshot or watery eyes
- blurry or decreased vision
- dry eyes
- excess debris along the eyelids or eyelashes
- gritty feeling, like you have sand or dust in your eyes
- itchy, burning, or stinging eyes
- red, swollen eyelids, which is the most common symptom
- sensitivity to light
- styes and chalazions
Ocular rosacea symptoms are usually mild. It is easy to mistake them for other conditions, such as allergies. Because of this, people with rosacea may not realize the disease is affecting their eyes. This is especially true for people who do not have skin symptoms yet.
What causes ocular rosacea?
The exact cause of rosacea, including ocular rosacea, is unclear. Researchers have linked
Possible associations include:
- genetics
- Demodex mites, which can clog skin pores and carry bacteria that can lead to inflammation
- environmental factors
- infections by Helicobacter pylori, a bacteria that cause infections in the digestive tract
- immune system reactions
- vascular problems, which result in blood and lymph vessel swelling
With microorganisms, it is unclear whether they are a cause or a consequence of rosacea.
There are also several things that can trigger a rosacea flare, including:
- aerobic exercise
- alcohol
- exposure to wind
- extreme temperatures
- hot beverages
- spicy food
- stress
- UV light
If you have rosacea, it is important to learn your triggers and to try to avoid them. This is a big step toward managing rosacea.
Try keeping a
Over time, this process may help you identify and steer clear of your rosacea triggers.
How do doctors diagnose ocular rosacea?
Rosacea is a
Because rosacea affects the skin, most people seek care from a dermatologist. If rosacea affects your eyes though, you should ask for a referral to an ophthalmologist. This doctor specializes in treating eye problems. An eye doctor will also tell you about special medicines and treatments that can help you cope with ocular rosacea.
What are the treatments for ocular rosacea?
There is no cure for rosacea, including ocular rosacea. Untreated ocular rosacea can lead to eyelid infections. Eye doctors can prescribe medicines that will fight these infections and ease other symptoms of the condition. Medications
- antibiotic eye ointment
- artificial tears to moisten and lubricate the eyes
- corticosteroid eyedrops and eye ointments to treat redness and swelling
- cyclosporine eyedrops
- oral antibiotics, which have
anti-inflammatory Trusted Source National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases Governmental authority Go to source effects at doses for rosacea treatment
Your eye doctor may want you to clean your eyelids gently several times a day. To do this, you use an over-the-counter eyelid cleanser or a mild baby shampoo. Applying a warm compress over your eyes several times a day also helps. This may ease symptoms and prevent infection.
Check with your eye doctor about intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy for ocular rosacea. This in-office procedure can target and constrict blood vessels that cause inflammation and redness of the eyelids.
IPL has been
What are the potential complications of ocular rosacea?
Untreated ocular rosacea can lead to
- Iritis: This is painful inflammation of the iris, the color part of the eye.
- Keratitis: This is an ulcer on the cornea, the clear outer layer of the eye.
- Scleritis: This inflammation of the sclera, the white of the eye.
Eventually, prolonged inflammation can lead to neovascularization of the cornea. This is the development of new blood vessels. Scarring in these areas of the eye can also happen. These effects can impair your vision. In severe cases, blindness can occur.
Summary
Ocular rosacea is a form of the inflammatory skin condition rosacea. It can occur before skin problems develop or at the same time. The main symptoms are redness and swelling of the eyelids. Eye irritation and infections can also occur.
Doctors do not fully understand what causes ocular rosacea, and there is no cure. However, treatment is available to manage symptoms.




