Ovarian cysts in premenopausal women are common and noncancerous in the vast majority of cases. They usually develop during the normal process of ovulation. It’s rare to for these cysts to be cancerous in this group of women. Cancerous cysts become more likely after menopause as women age. However, ovarian cancer is still a relatively rare cancer, accounting for about 3% of cancers affecting American women.
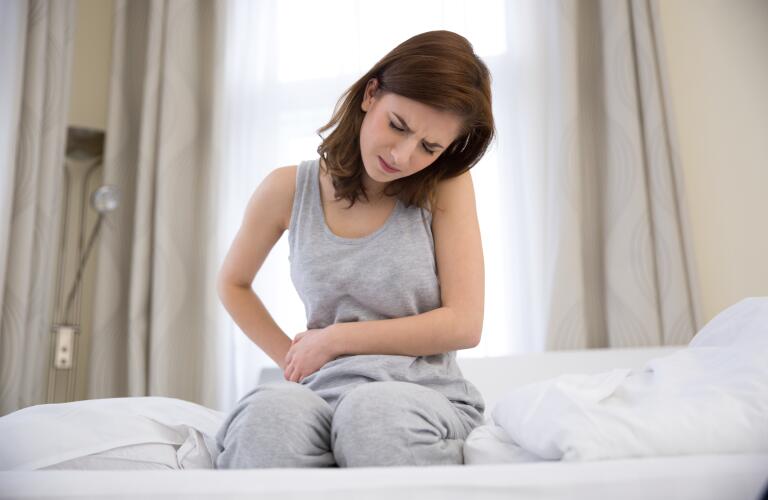
The symptoms of ovarian cysts and ovarian cancer are very similar. This makes it very important to see your doctor in order to get the right diagnosis.
Most ovarian cysts do not cause symptoms. When symptoms develop, they can include:
Bloating
Nausea or vomiting
Pain on one side of the lower abdomen. The pain ranges from dull to sharp and may worsen with certain activities, such as sex or bowel movements. It may also come and go.
Pressure in the abdomen
See your doctor for a diagnosis if you have any of these symptoms.
If a large cyst ruptures, it can be a medical emergency because it can cause heavy bleeding. The bleeding can be internal, so you may not see it. Seek immediate medical care or call 911 if you have symptoms including:
Rapid breathing
Severe abdominal pain with or without nausea, vomiting or fever
Ovarian cancer can be hard to detect. The ovaries lie deep in the abdomen, making it virtually impossible to find tumors in early stages. There are also no reliable screening tests. Symptoms usually don’t develop until ovarian cancer is in advanced stages and they tend to be vague. Symptoms can include:
Abdominal, pelvic or back pain
Bloating or a feeling of fullness in the abdomen
Menstrual changes or abnormal vaginal bleeding
Pain during sex
Trouble eating, feeling full quickly, or upset stomach
Urinary symptoms such as having to go frequently or urgently
Other conditions share many of the same symptoms. See your doctor if any of these symptoms persist for more than two weeks. Whatever the cause, seeking early treatment offers the best chance for successful treatment.