Research has shown a chronic cough lasting more than eight weeks is linked to severe cases of asthma.
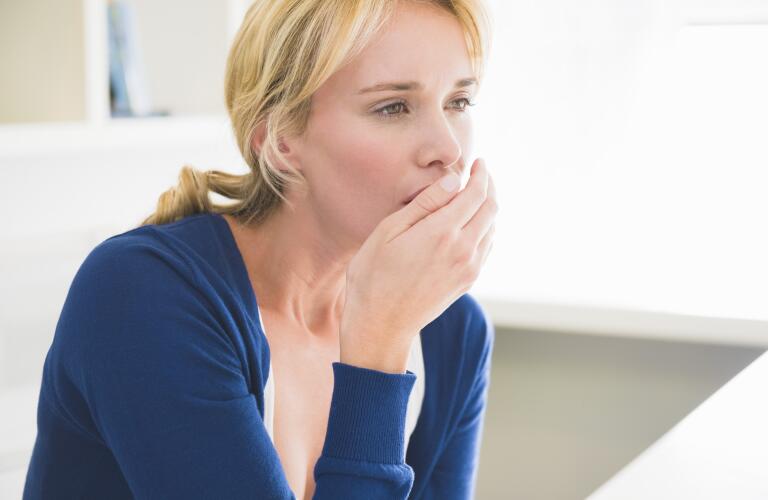

Do you have asthma and can’t stop coughing? It may be something to take note of. Although a cough is a common symptom of asthma, if you find yourself coughing frequently, your asthma may be considered severe. It's important to treat severe asthma appropriately.
A study compared patients with asthma and chronic cough to those with asthma who don’t have chronic cough. Patients with chronic cough were found to experience more respiratory symptoms, including:
- wheezing
- difficulty breathing, both day and night
- mucus production
- chest tightness or pain
Lung function was tested in both groups. Asthmatics with chronic cough tended to have significantly worse lung strength and volume than those without chronic cough. The chronic cough group also had more frequent illness and doctor’s visits. They were more likely to have had bronchitis or pneumonia at least six times in the last 10 years and visited the doctor more than three times in the last year.
Researchers also examined blood samples from patients in both groups. Individuals with asthma and chronic cough had higher levels of neutrophils, leukocytes, and fibrinogen in their blood. These are indicators of inflammation within the body and are associated with severe asthma.
Based on these findings, researchers concluded that asthma patients with chronic cough tended to have a more severe form of the disease.
Severe asthma is difficult to control. If you have it, you’ll require high levels of treatment, including inhaled steroids, systemic steroids, and other control medications. Even with treatment, you may still have frequent symptoms, impacting your ability to work, attend school, or simply enjoy your daily activities.
Luckily, our understanding of severe asthma has grown in recent years. Researchers have learned there are different types of asthma, leading to the development of new, more personalized treatments. Working with a specialist to identify what type of severe asthma you have is helpful in selecting the best treatment options for you.
Some types of severe asthma include:
- Allergic asthma: An allergen, such as pollen or dust, may cause your body to release a substance called Immunoglobulin E (IgE). IgE can trigger inflammation in your airways and cause an asthma attack. Blood tests to measure IgE can determine if you have allergic asthma. Special biologic medications may be helpful. Biologics are newer medicines, derived from living organisms, that can block various sources of inflammation at their root. A biologic called omalizumab (Xolair) blocks IgE and in select patients may ease symptoms for people with allergic asthma.
- Eosinophilic asthma: Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell. For some people, high levels of eosinophils can cause airway inflammation. Certain biologic medications may be prescribed to lower the amount of eosinophils in your blood. Examples are mepolizumab (Nucala) and dupilumab (Dupixent).
- Neutrophilic asthma: A different type of white blood cell, called a neutrophil, may lead to inflammation and asthma symptoms in some cases. This type of asthma doesn’t respond well to inhaled steroids and is often associated with infections. Proper treatment may involve the use of short-term macrolide antibiotics.
If you’ve had an ongoing cough or feel like you are struggling to manage your asthma symptoms, schedule an appointment with your doctor. Asthma medications may need to be adjusted over time, and with more options available than ever before, even severe asthma can be better controlled.