10 Conditions Diagnosed With an EEG

Medically Reviewed By William C. Lloyd III, MD, FACS
Written By Sarah Lewis, PharmD on November 3, 2020
-
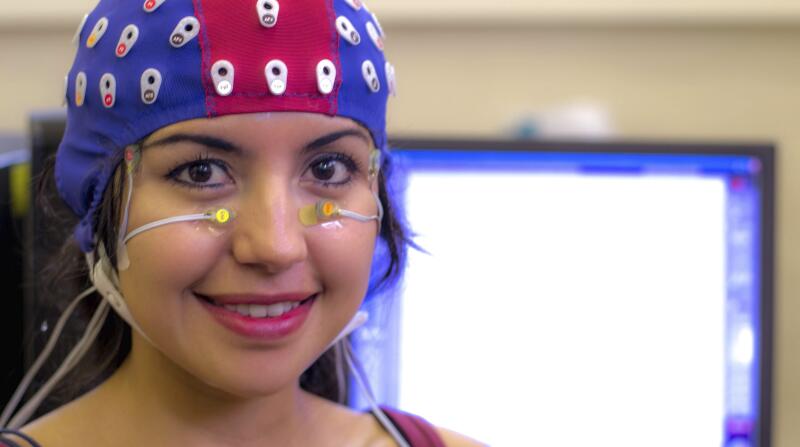
 An EEG test is a record of brain activity.Electroencephalography (EEG)—is a test that measures the electrical activity of the brain. An EEG involves attaching electrodes to your scalp to record electrical activity. The EEG test and electrodes are painless. Your doctor may recommend this test to help diagnose neurological conditions. Read on to learn about conditions that doctors may diagnose with an EEG.
An EEG test is a record of brain activity.Electroencephalography (EEG)—is a test that measures the electrical activity of the brain. An EEG involves attaching electrodes to your scalp to record electrical activity. The EEG test and electrodes are painless. Your doctor may recommend this test to help diagnose neurological conditions. Read on to learn about conditions that doctors may diagnose with an EEG. -
 1. Seizure DisordersThe primary use of EEG is diagnosing epilepsy and other seizure disorders. Epilepsy is a brain disorder marked by seizures, muscle spasms, and strange behavior or emotions. Experts don’t fully understand what causes epilepsy. It may involve abnormal nerve cell connections and chemical imbalances in the brain. The main treatment for epilepsy is anti-seizure medication. Brain surgery is a treatment for some seizure disorders.
1. Seizure DisordersThe primary use of EEG is diagnosing epilepsy and other seizure disorders. Epilepsy is a brain disorder marked by seizures, muscle spasms, and strange behavior or emotions. Experts don’t fully understand what causes epilepsy. It may involve abnormal nerve cell connections and chemical imbalances in the brain. The main treatment for epilepsy is anti-seizure medication. Brain surgery is a treatment for some seizure disorders. -
-
 2. Sleep DisordersSleep disorders range from insomnia to narcolepsy. People with insomnia have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep. Triggers include stress, trauma, and certain medical conditions or medicines. Lifestyle changes and better sleep hygiene can help. Narcolepsy is marked by extreme daytime sleepiness and uncontrollable bouts of daytime sleep. Experts believe low levels of a brain chemical—hypocretin—may be a cause of narcolepsy. Doctors may prescribe medicines to treat narcolepsy and chronic insomnia.
2. Sleep DisordersSleep disorders range from insomnia to narcolepsy. People with insomnia have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep. Triggers include stress, trauma, and certain medical conditions or medicines. Lifestyle changes and better sleep hygiene can help. Narcolepsy is marked by extreme daytime sleepiness and uncontrollable bouts of daytime sleep. Experts believe low levels of a brain chemical—hypocretin—may be a cause of narcolepsy. Doctors may prescribe medicines to treat narcolepsy and chronic insomnia. -
 3. Brain TumorsThere are many types of brain tumors. They can be cancerous (malignant) and noncancerous (benign). Symptoms of a brain tumor can include headaches, seizures, sensory changes, movement problems, fatigue, and behavior changes. Experts don’t fully understand what causes most brain tumors. Doctors treat brain tumors with surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Rehabilitation is a vital part of recovery for most people.
3. Brain TumorsThere are many types of brain tumors. They can be cancerous (malignant) and noncancerous (benign). Symptoms of a brain tumor can include headaches, seizures, sensory changes, movement problems, fatigue, and behavior changes. Experts don’t fully understand what causes most brain tumors. Doctors treat brain tumors with surgery, radiation and chemotherapy. Rehabilitation is a vital part of recovery for most people. -
 4. Brain InjuryA brain injury can be traumatic—from external force—or acquired—often due to stroke or lack of oxygen to the brain. Symptoms depend on the severity of the damage, but range from headache and balance problems to loss of consciousness and coma. Basic treatment includes rest and avoiding physical and mental activity like reading. People who lose mental function will need more extensive therapy. Lifelong therapy may be necessary for moderate and severe brain injuries.
4. Brain InjuryA brain injury can be traumatic—from external force—or acquired—often due to stroke or lack of oxygen to the brain. Symptoms depend on the severity of the damage, but range from headache and balance problems to loss of consciousness and coma. Basic treatment includes rest and avoiding physical and mental activity like reading. People who lose mental function will need more extensive therapy. Lifelong therapy may be necessary for moderate and severe brain injuries. -
 5. DementiaDementia is memory loss and impaired mental ability, such as thinking and speaking. Problems with behavior can also occur. Dementia occurs with various conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and vascular dementia. Doctors treat dementia with medication to help with memory and thinking skills. They also use techniques to manage behavioral problems. However, medications will not reverse the changes in the brain that are causing dementia.
5. DementiaDementia is memory loss and impaired mental ability, such as thinking and speaking. Problems with behavior can also occur. Dementia occurs with various conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and vascular dementia. Doctors treat dementia with medication to help with memory and thinking skills. They also use techniques to manage behavioral problems. However, medications will not reverse the changes in the brain that are causing dementia. -
-
 6. Brain InfectionsBrain infections include conditions like a brain abscess and encephalitis—an inflammation of the brain that can be due to an infection. Brain infections can cause headaches, seizures, changes in mental state, and changes in behavior or personality. Usually, an infection spreads to the brain from other parts of the body. Doctors treat brain infections with antibiotics, antiviral medicines, anti-inflammatory medicines, and surgery if necessary.
6. Brain InfectionsBrain infections include conditions like a brain abscess and encephalitis—an inflammation of the brain that can be due to an infection. Brain infections can cause headaches, seizures, changes in mental state, and changes in behavior or personality. Usually, an infection spreads to the brain from other parts of the body. Doctors treat brain infections with antibiotics, antiviral medicines, anti-inflammatory medicines, and surgery if necessary. -
 7. StrokeA stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted and brain cells die. Signs of a stroke include sudden paralysis or weakness, numbness, drooping face, changes in speech, or trouble understanding words. Strokes happen when a clot blocks a blood vessel (ischemic stroke) or a blood vessel bursts and bleeds into the brain (hemorrhagic stroke). Stroke requires emergency treatment.
7. StrokeA stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted and brain cells die. Signs of a stroke include sudden paralysis or weakness, numbness, drooping face, changes in speech, or trouble understanding words. Strokes happen when a clot blocks a blood vessel (ischemic stroke) or a blood vessel bursts and bleeds into the brain (hemorrhagic stroke). Stroke requires emergency treatment. -
 8. Attention DisordersAttention disorders include conditions like attention deficit disorder (ADD) and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). They are marked by difficulty paying attention, staying focused, and controlling behavior. Experts don’t fully understand what causes attention disorders. Genes may play a role. Doctors treat attention disorders with medicines, behavioral therapy, and social skills training.
8. Attention DisordersAttention disorders include conditions like attention deficit disorder (ADD) and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). They are marked by difficulty paying attention, staying focused, and controlling behavior. Experts don’t fully understand what causes attention disorders. Genes may play a role. Doctors treat attention disorders with medicines, behavioral therapy, and social skills training. -
 9. Behavior DisordersBehavior disorders include conditions like oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder. An EEG can help determine if there is a physical cause of these disorders. Behavior disorders are disruptive and interfere with school, work, family, and social relationships. People who suffer from these disorders benefit from behavioral therapy. Doctors also use medications in some cases.
9. Behavior DisordersBehavior disorders include conditions like oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder. An EEG can help determine if there is a physical cause of these disorders. Behavior disorders are disruptive and interfere with school, work, family, and social relationships. People who suffer from these disorders benefit from behavioral therapy. Doctors also use medications in some cases. -
 10. Developmental DelaysDevelopmental delays affect motor skills, communication, and thinking skills. Kids with developmental delays miss or lose normal milestones, such as walking and talking. An EEG may help identify a physical cause of delays in these children. Treatment focuses on a child’s individual needs. This may include speech therapy, physical therapy, occupational therapy, behavioral therapy, and social skills training.
10. Developmental DelaysDevelopmental delays affect motor skills, communication, and thinking skills. Kids with developmental delays miss or lose normal milestones, such as walking and talking. An EEG may help identify a physical cause of delays in these children. Treatment focuses on a child’s individual needs. This may include speech therapy, physical therapy, occupational therapy, behavioral therapy, and social skills training.
Conditions an EEG Test Can Diagnose: Neurological Conditions & Brain Diseases