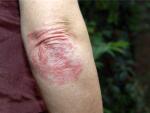
Burns

Burns involve damage to your skin, typically due to heat. There are different types of burns. However, they may cause similar pain as well as:
- skin peeling
- redness or discoloration
- blisters
- area swelling
- white or charred skin
Sunburns
Sunburns result in damage to your skin from exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Overexposure and unprotected exposure to the sun can lead to:
- premature wrinkles and aging
- age spots
- increased risk of skin cancer
Symptoms of a sunburn typically begin around
Skin peeling due to a sunburn typically begins around 3–8 days after the initial exposure.
Tips for sunburn prevention
- Cover up.
- Apply sunscreen that has a sun protection factor of 30 or higher.
- Reapply sunscreen every 2 hours.
- Seek out the shade.
- Wear a hat and sunglasses.
- Avoid indoor tanning beds.
Read about home remedies for sunburn relief.
Chemical burn
Chemical burns result from exposure to acid or other chemicals. Experts consider them a medical emergency. If you experience a burn after exposure to any chemical, get medical care right away.
Symptoms of a chemical burn include:
- redness or discoloration, irritation, and burning at the contact area
- pain or numbness in the affected site
- formation of black dead skin
Thermal burn
Thermal burns
- hot surfaces
- scalding liquids
- steam
- flames
Eczema
Eczema is an inflammatory skin condition. There are several types of eczema, and it is a common skin condition. Around 31 million people in the United States experience eczema.
Itchy skin is the most typical symptom of eczema. Other symptoms include:
- dry, sensitive skin
- inflamed skin
- discoloration
- rough or scaly patches of skin that can flake off
- crustiness or oozing
- areas of swelling
Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a type of eczema. It results from contact with a certain substance. One of the
Symptoms of contact dermatitis include:
- skin inflammation and discoloration
- blisters
- dry skin
- thickened or cracked skin
- sensation of itching, burning, or stinging
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic form of eczema. It typically appears on areas of the body with oil, like the:
- scalp
- nose
- upper back
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis include:
- scaly skin patches
- redness or discoloration beneath skin patches
- skin patches appearing greasy or moist
- yellowish-white scales that tend to flake off
Toxic shock syndrome
Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is a rare yet potentially life threatening condition. It results from an infection due to certain types of bacteria.
Symptoms of TSS typically come on suddenly and worsen quickly. Early diagnosis and treatment are important as TSS can quickly become fatal. The symptoms include:
- fever
- flu-like symptoms, such as:
- headache
- body aches
- sore throat
- tiredness
- widespread sunburn-like rash
- whites of your eyes, lips, and tongue turning red
- dizziness or fainting
- difficulty breathing
- confusion
- patches of peeling skin on your hands and feet
Athlete’s foot
Athlete’s foot is an infection of the feet and skin due to various types of fungi. It
Athlete’s foot is typically spread through skin-to-skin contact or by coming into contact with the fungi in damp areas like:
- showers
- locker rooms
- swimming pools
Symptoms of athlete’s foot include:
- red or discolored skin
- cracked and flaky skin
- itchiness
- white thickened skin
- area swelling
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is
Plaque psoriasis is the most common type. Symptoms of plaque psoriasis include:
- raised and inflamed patches of scaly skin that may flake off
- itchiness
- pain
- red with a silvery-white buildup on skin with less pigment
- purple, grayish, or dark brown and thicker patches on skin with more pigment
These scaly plaques of skin can appear anywhere on the body. However, they are often on the:
- scalp
- knees
- elbows
- torso
Read about managing my psoriasis.
What are other causes of skin peeling?
There are many other causes of skin peeling. These include:
- ringworm
- irritation
- allergic reaction
- immune system disorders
- some cancer treatments
- certain medications
- Kawasaki disease
- peeling skin syndrome
- staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome or Ritter disease
When should you contact a doctor for skin peeling?
Some causes of peeling skin, like sunburn, are easily treatable at home. However, a doctor needs to diagnose many of the other causes.
If you experience symptoms of psoriasis, eczema, TSS, and other conditions, contact your doctor. For many conditions that can cause skin peeling, that is only one aspect of it, and your doctor can recommend the most effective treatment.
If you have peeling skin and experience symptoms of infection, contact your doctor right away.
Symptoms of infection
How can you treat skin peeling?
Treatment for skin peeling depends on the underlying cause. Speak with your doctor to find the most effective treatment for your circumstances.
Some treatments for peeling skin may include:
- moisturizing the skin
- staying hydrated
- taking antibiotics
- using antifungal creams
- avoiding scratching or peeling the skin
Can you prevent skin peeling?
Some causes of skin peeling like eczema, psoriasis, and other conditions are not preventable. However, conditions like sunburn, athlete’s foot, and contact dermatitis are preventable.
To prevent contact dermatitis, try to avoid exposure to the substance that causes your reaction.
To prevent athlete’s foot, try the following:
- Keep your nails short and clean.
- Avoid walking barefoot in public showers and locker rooms and sharing towels, shoes, or socks.
- Wear loose shoes.
- Clean and dry your feet thoroughly after you shower or bathe.
Summary
There are many possible causes of skin peeling. These range from sunburn to psoriasis. Some causes are preventable, and many are treatable.
Because there are so many causes of peeling skin, contact your doctor if you have new areas of peeling skin that are not due to something like a sunburn.
If you experience symptoms of infection, like fever, discharge from your skin, and increased pain, contact your doctor right away.